User Guide
Welcome to Duke: Martin’s Todo Helper!
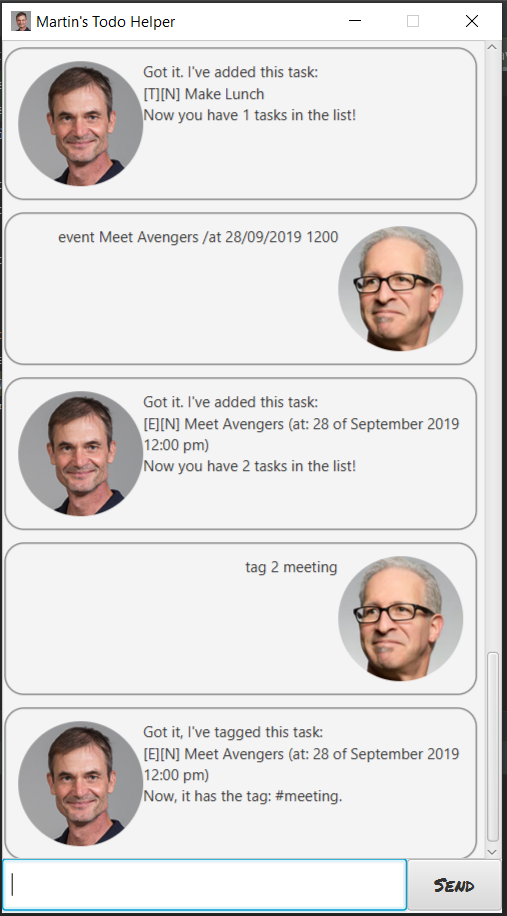
To help you understand this application, there a few things you would need to set up before proceeding with usage.
Contents Page
Prerequisites
1) Have Java installed on your computer.
2) Create a folder called data in the same directory in which
you save the jar file for the application for data storage
and processing.
Do also make sure that there is a tasks.txt
Text Document file inside the folder!

Features
Here are the following features which can aid you in the usage of this to-do list application.
Feature 1: Adding of Tasks
You are allowed to create the following types of tasks. 1) ToDo Tasks with a name. 2) Deadline Tasks with a name and a specified deadline (time). 3) Event Tasks with a name and a specified time.
Feature 2: Editing of Tasks
You are allowed to edit the following: 1) The name of the task 2) The date and time of the task. (Only applies to deadline and event tasks)
Feature 3: Completion of Tasks
You are allowed to mark tasks as done.
Feature 4: Deletion of Tasks
You are allowed to delete tasks.
Feature 5: Tagging of Tasks
You are allowed to tag tasks for easier reference.
Feature 6: Searching of Tasks
You are allowed to search tasks based on either criteria: 1) A keyword which is found within the task name. 2) The tag of the tasks.
Feature 7: Listing of Tasks
You are allowed to list the tasks you have in the application.
Feature 8: Listing of Commands
You are allowed to list the commands available in the application.
Feature 9: Loading and Saving of Tasks
The tasks processed will be saved automatically if you have
your data folder in the same subdirectory as your jar file.
On restarting the application, the file data/tasks.txt will
be loaded and processed to load the tasks stored in it.
Usage
These are the following commands to aid you through in the usage of this application.
bye - Indicate the exit of the application
Once typed in, you will receive a prompt to leave the application. Following which, press enter to exit the application.
Example of usage:
bye
Expected outcome:
Receives a prompt to leave the application
deadline - Creates a new deadline task
After providing the task name and deadline date and time, a new deadline task will be created.
Date must be in the format of dd/mm/yyyy
Time must be in format of hhmm
Example of usage:
deadline (taskname) /by (date) (time)
Expected outcome:
Creates a new deadline task based on name and deadline
delete - Deletes a task from the list of tasks
After the providing the task number, the specified task will be deleted as such.
The task number is 1-indexed, so the first task has
the index of 1.
Example of usage:
delete (index)
Expected outcome:
Deletes the task at the specified index
done - Marks a task as done
After providing the index of the task, the task will be marked as done.
The task number is 1-indexed, so the first task has
the index of 1.
Example of usage:
done (index)
Expected outcome:
Marks the specified task as done
edit date - Edits the date of the task
After providing the index and the new date, the specified task will have its date changed.
The task number is 1-indexed, so the first task has
the index of 1.
Date must be in the format of dd/mm/yyyy
Time must be in format of hhmm
Example of usage:
edit date (index) (date) (time
Expected outcome:
Edits the date and time of the task at the specified index
edit name - Edits the name of the task
After providing the index and the new name, the specified task will have its name changed.
The task number is 1-indexed, so the first task has
the index of 1.
Example of usage:
edit name (index) (name)
Expected outcome:
Edits the name of the task at the specified index
event - Creates a new event task
After providing the task name and event date and time, a new event task will be created.
Date must be in the format of dd/mm/yyyy
Time must be in format of hhmm
Example of usage:
event (taskname) /at (date) (time)
Expected outcome:
Creates a new event task based on name and date and time
find - Finds tasks containing keywords
After providing the keyword, a list of tasks will be given which contain the specific keywords.
Example of usage:
find (keywords)
Expected outcome:
Returns a list of tasks containing the keywords
findTag - Finds tasks containing the tag
After providing the tag, a list of tasks will be given which contain the specific tag.
Example of usage:
findTag (tag)
Expected outcome:
Returns a list of tasks containing the tag
help - Provides the list of commands
On this command, a list of commands will be given.
Example of usage:
help
Expected outcome:
Returns a list of commands available
list - Provides the list of tasks
On this command, a list of tasks will be given.
Example of usage:
list
Expected outcome:
Returns the list of tasks
tag - Gives a tag to a task
On providing the task number and the tag, the tag will be given to that task.
The task number is 1-indexed, so the first task has
the index of 1.
Example of usage:
tag (index) (tag)
Expected outcome:
Gives a tag to the specified task
todo - Creates a new todo task
After providing the task name, a new todo task will be created.
Example of usage:
todo (taskname)
Expected outcome:
Create a new todo task based on the given name